Solution.82 Remove Duplicates from Sorted List II
82. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List II
Solved
Medium
Topics
Companies
Given the head of a sorted linked list, delete all nodes that have duplicate numbers, leaving only distinct numbers from the original list. Return the linked list sorted as well.
Example 1:
Input: head = [1,2,3,3,4,4,5]
Output: [1,2,5]
Example 2:
Input: head = [1,1,1,2,3]
Output: [2,3]The number of nodes in the list is in the range [0, 300].
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
The list is guaranteed to be sorted in ascending order.
range = 300 개 이므로 시간 복잡도는 넉넉히 존재가능하다.
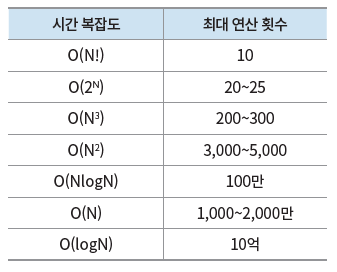
위 표는 1초 동안 수행할 수 있는 최대 연산 횟수를 기준으로, 시간 복잡도를 분석한 결과를 나타낸다. 즉, 입력 크기가 300 이하일 때, 최적의 해결법을 찾기 위해 O(N3) 이상의 시간 복잡도를 고려해야 한다는 의미다.
풀이
- 시간 복잡도: O(N)
- 공간 복잡도: O(N)
시간 제한을 엄격히 두어 결국 문제를 풀지 못한 채 종료되었다. 접근 방식은 유사했지만, 마지막 마무리를 짓지 못한 점이 아쉬웠다.
이 문제에서 핵심은 ListNode를 이전(prev), 현재(curr), 다음(next) 총 세 개를 관리하며 비교하는 것이다. 만약 현재 노드(curr)와 다음 노드(next)의 값이 같다면, 이전 노드(prev)를 활용해 현재 노드를 삭제하고, 이후 노드들과 계속 비교해 나가는 것이 중요하다.
결국, 값을 어떻게 삭제하느냐에 따라 해결 방식이 달라지며, 삭제 과정만 명확하면 이후의 로직은 자연스럽게 동작한다.
class Solution:
def deleteDuplicates(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
# Iterative T.C O(N) & S.C O(1)
dummy = ListNode(-1)
dummy.next = head
prev, curr = dummy, head
while curr:
if curr.next and curr.next.val == curr.val:
while curr.next and curr.next.val == curr.val:
curr = curr.next
prev.next = curr.next
else:
prev = prev.next
curr = curr.next
return dummy.next
'IT > 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| LeetCode - P.6 (0) | 2025.03.25 |
|---|